%% 1-1 在命令行窗口中输入两个矩阵,进行各个矩阵运算
A = magic(3) % 创建一个3阶魔方矩阵
B = [1 8 9;6 7 12;0 3 11] % 创建一个自定义的3阶矩阵
A + B % 矩阵的加法运算
A - B % 矩阵的减法运算
flipud(A) % 矩阵的上下翻转运算
fliplr(A) % 矩阵的左右翻转运算
%% 实验结果
% ex1_1
% A =
% 8 1 6
% 3 5 7
% 4 9 2
% B =
% 1 8 9
% 6 7 12
% 0 3 11
% ans =
% 9 9 15
% 9 12 19
% 4 12 13
% ans =
% 7 -7 -3
% -3 -2 -5
% 4 6 -9
% ans =
% 4 9 2
% 3 5 7
% 8 1 6
% ans =
% 6 1 8
% 7 5 3
% 2 9 4

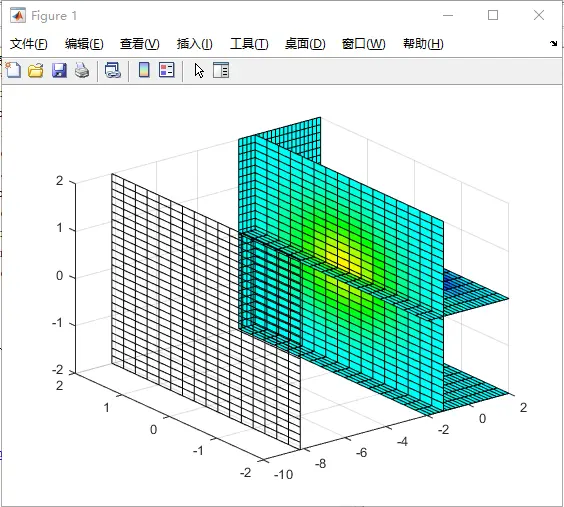
%% 1-2 利用MATLAB绘制三维切片图
clear all;
[x,y,z] = meshgrid(-2:0.2:2, -2:0.25:2, -2:0.16:2); % 三维网格图,x轴为-2到2,间隔为0.2,y轴为-2到2,间隔为0.2,z轴为-2到2,间隔为0.16
v = x .* exp(- x .^ 2 - y .^ 2 - z.^2); % 画出它的三维函数的值(是一个平面)
xslice = [-1.2, -8.2]; % x轴切片
yslice = 2; % y轴切片
zslice = [-2, 0]; % z轴切片
slice(x,y,z,v,xslice,yslice,zslice) % 切片
colormap hsv % 改变色彩搭配为hsv型
set(gcf, 'color', 'w') % 设置图片的背景为白色
%% 实验结果

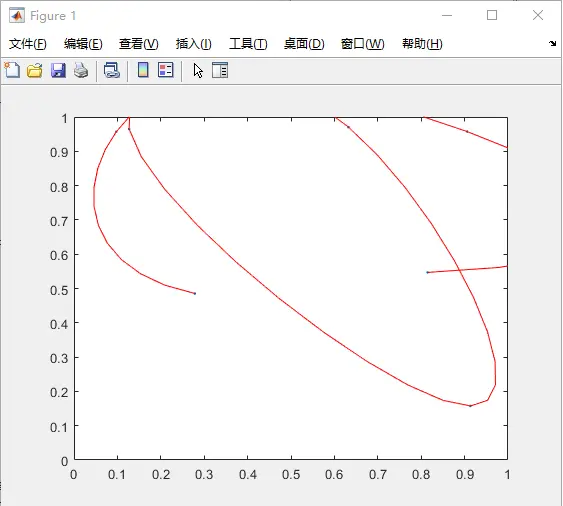
%% 1-3 对给定的数据进行拟合
clear all; % 清除所有
n = 7;
x = rand(n,1); % 满足N(0,1)分布的随机数
y = rand(n,1); % 满足N(0,1)分布的随机数
plot(x,y,'.'); % 画图
axis([0 1 0 1]); % 坐标轴
t = 1:n;
ts = 1:1/10:n;
xs = spline(t,x,ts); % 三次方样条插值
ys = spline(t,y,ts); % 三次方样条插值
hold on; % 在原本已有图片的基础上画图
plot(xs,ys,'r'); % 画图
hold off; % 解除在原本已有图片的基础上画图
%% 实验结果

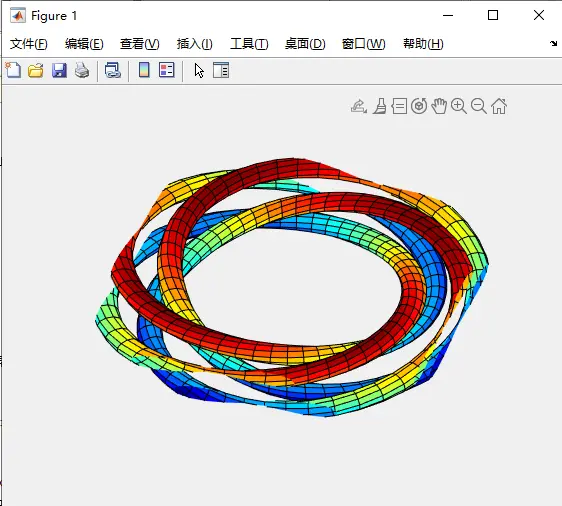
%% 1-4 绘制4个首尾相接的圆环
clear all;
ab = [0 2*pi];
rtr = [6 1 1];
pq = [10 50];
box = [-6.6 6.6 -6.6 6.6 -3 3];
vue = [200 70];
tube('xylink1a',ab,rtr,pq,box,vue);
colormap(jet);
hold on;
tube('xylink1b',ab,rtr,pq,box,vue);
tube('xylink1c',ab,rtr,pq,box,vue);
tube('xylink1d',ab,rtr,pq,box,vue);
hold off;
%% 有一说一,这个文档的含义我也不清楚,特别是tube函数的意思
% tube Generating function for Edward's parametric curves.
% tube(xy,ab,rtr,pq)) takes the following arguments:
%
% xy = string name of function [xt,yt] = xy(t)
% defining parametric curve to be revolved
% ab = [a b] = interval of defn of parametric curve
% rtr = [radius twist revs] for revolution of curve
% pq = [p q] = numbers of t- and u-subintervals
% box = [x1 x2 y1 y2 z1 z2] for viewing tube
%% 实验结果

%% 1-5 利用help命令查询elmat(类)名的帮助
help elmat
%% 实验结果
% ex1_5
% Elementary matrices and matrix manipulation.
%
% Elementary matrices.
% zeros - Zeros array.
% ones - Ones array.
% eye - Identity matrix.
% repmat - Replicate and tile array.
% repelem - Replicate elements of an array.
% linspace - Linearly spaced vector.
% logspace - Logarithmically spaced vector.
% freqspace - Frequency spacing for frequency response.
% meshgrid - X and Y arrays for 3-D plots.
% accumarray - Construct an array with accumulation.
% : - Regularly spaced vector and index into matrix.
%
% Basic array information.
% size - Size of array.
% length - Length of vector.
% ndims - Number of dimensions.
% numel - Number of elements.
% disp - Display matrix or text.
% isempty - True for empty array.
% isequal - True if arrays are numerically equal.
% isequaln - True if arrays are numerically equal, treating NaNs as equal.
% height - Number of rows.
% width - Number of columns.
%
% Matrix manipulation.
% cat - Concatenate arrays.
% reshape - Reshape array.
% diag - Diagonal matrices and diagonals of matrix.
% blkdiag - Block diagonal concatenation.
% tril - Extract lower triangular part.
% triu - Extract upper triangular part.
% fliplr - Flip matrix in left/right direction.
% flipud - Flip matrix in up/down direction.
% flip - Flip the order of elements.
% rot90 - Rotate matrix 90 degrees.
% : - Regularly spaced vector and index into matrix.
% find - Find indices of nonzero elements.
% end - Last index.
% sub2ind - Linear index from multiple subscripts.
% ind2sub - Multiple subscripts from linear index.
% bsxfun - Binary singleton expansion function.
%
% Multi-dimensional array functions.
% ndgrid - Generate arrays for N-D functions and interpolation.
% permute - Permute array dimensions.
% ipermute - Inverse permute array dimensions.
% shiftdim - Shift dimensions.
% circshift - Shift array circularly.
% squeeze - Remove singleton dimensions.
%
% Array utility functions.
% isscalar - True for scalar.
% isvector - True for vector.
% isrow - True for row vector.
% iscolumn - True for column vector.
% ismatrix - True for matrix.
%
% Special variables and constants.
% eps - Floating point relative accuracy.
% realmax - Largest positive floating point number.
% realmin - Smallest positive floating point number.
% intmax - Largest positive integer value.
% intmin - Smallest integer value.
% flintmax - Largest consecutive integer in floating point format.
% pi - 3.1415926535897....
% i - Imaginary unit.
% inf - Infinity.
% nan - Not-a-Number.
% isnan - True for Not-a-Number.
% isinf - True for infinite elements.
% isfinite - True for finite elements.
% j - Imaginary unit.
% true - True array.
% false - False array.
%
% Specialized matrices.
% compan - Companion matrix.
% gallery - Test matrices.
% hadamard - Hadamard matrix.
% hankel - Hankel matrix.
% hilb - Hilbert matrix.
% invhilb - Inverse Hilbert matrix.
% magic - Magic square.
% pascal - Pascal matrix.
% rosser - Classic symmetric eigenvalue test problem.
% toeplitz - Toeplitz matrix.
% vander - Vandermonde matrix.
% wilkinson - Wilkinson's eigenvalue test matrix.

%% 1-6 利用help命令查询power(函数)的帮助
help power
%% 实验结果
% ex1_6
% power - 按元素求幂
% 此 MATLAB 函数 计算 A 中每个元素在 B 中对应指数的幂。A 和 B 的大小必须相同或兼容。
%
% C = A.^B
% C = power(A,B)
%
% 另请参阅 realpow, mpower, nthroot
%
% power 的文档

%% 1-7 利用lookfor命令查询power(函数)的帮助信息
lookfor power
%% 实验结果
% ex1_6 - 1-6 利用help命令查询power(函数)的帮助
% ex1_7 - 1-7 利用lookfor命令查询power(函数)的帮助信息
% nextpow2 - Next higher power of 2.
% pow2 - Base 2 power and scale floating point number.
% realpow - Real power.
% openppt - Opens a Microsoft PowerPoint file.
% normest1 - Estimate of 1-norm of matrix by block 1-norm power method.
% normAm - Estimate of 1-norm of power of matrix.
% mpower - ^ Matrix power.
% power - .^ Array power.
% mxdom2ppt - Create a PowerPoint presentation.

%% 1-8 利用which命令查询power帮助信息
which power -all
%% 实验结果
% ex1_8
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@char\power) % char method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@double\power) % Shadowed double method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@int16\power) % Shadowed int16 method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@int32\power) % Shadowed int32 method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@int64\power) % Shadowed int64 method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@int8\power) % Shadowed int8 method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@logical\power) % Shadowed logical method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@single\power) % Shadowed single method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@uint16\power) % Shadowed uint16 method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@uint32\power) % Shadowed uint32 method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@uint64\power) % Shadowed uint64 method
% built-in (E:\MATLAB\R2021a\toolbox\matlab\ops\@uint8\power) % Shadowed uint8 method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed FilePathState method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.reference.property.RefEntityType method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.reference.api.EntityPrecision method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.reference.property.DeprecationStatus method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.reference.property.FunctionType method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.reference.api.EntityCaseSensitivity method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.lang.OnOffSwitchState method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.timer.CallBackTypeEnum method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.timer.BusyModeEnum method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.timer.ExecutionModeEnum method
% power is a built-in method % Shadowed matlab.internal.lang.capability.Capability method

%% 1-9 在命令窗口中计算tan(2*pi)
pi
tan(2*pi)
%% 实验结果
% exp1_9
% ans =
% 3.1416
% ans =
% -2.4493e-16

%% 1-10 利用isvarname函数验证各函数名是否正确
isvarname foo % foo是一个合格的函数名
isvarname 1th_column % 1th_column开头是数字1,不是合格的函数名
d = date; % 日期字符串,在今天会输出'30-Jun-2021'
isvarname(['Wednesday', d(1:2)]) % 中括号里面是字符串的含义为字符串的拼接
% d(1:2)则为字符串里面的第1、2个字符
%% 实验结果
% ex1_10
% ans =
% logical
% 1
% ans =
% logical
% 0
% ans =
% logical
% 1

%% 1-11 通过转换函数创建整数类型
clear all; % 清除MATLAB原空间变量
a = 109; % 默认为double型
b = 111.264; % 默认为double型
c = -23.19; % 默认为double型
A = int8(a) % 将double型的a强制转换为int8型
B = int16(a) % 将double型的b强制转换为int16型
C = int32(a) % 将double型的c强制转换为int32型
str = 'MATLAB~~~@!!' % 字符串(默认为char型)
D = int8(str) % 将字符串型的变量强制转换成int8型
whos % 查看各变量类型
%% 实验结果
% ex1_11
% A =
% int8
% 109
% B =
% int16
% 109
% C =
% int32
% 109
% str =
% 'MATLAB~~~@!!'
% D =
% 1×12 int8 行向量
% 77 65 84 76 65 66 126 126 126 64 33 33
% Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
%
% A 1x1 1 int8
% B 1x1 2 int16
% C 1x1 4 int32
% D 1x12 12 int8
% a 1x1 8 double
% b 1x1 8 double
% c 1x1 8 double
% str 1x12 24 char

%% 1-12 数据的取整
clear all; % 清空数据
a = [-1.9, -0.2, 3.4, 5.6, 7, 2.5];
A = round(a) % 四舍五入取整,如果小数部分为0.5就向绝对值大的方向取整
B = ceil(a) % 向上取整
C = fix(a) % 向下取整
D = floor(a) % 向0取整
%% 实验结果
% ex1_12
% A =
% -2 0 3 6 7 3
% B =
% -1 0 4 6 7 3
% C =
% -1 0 3 5 7 2
% D =
% -2 -1 3 5 7 2

%% 1-13 浮点数据转换函数展示
clear all;
a = 6.398;
A = single(a) % 将double类型的变量强制转换为single型并赋值给A
b = uint32(10056) % b为32位无符号整数
B = double(b) % 转成double类型
whos
%% 实验结果
% ex1_13
% A =
% single
% 6.3980
% b =
% uint32
% 10056
% B =
% 10056
% Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
%
% A 1x1 4 single
% B 1x1 8 double
% a 1x1 8 double
% b 1x1 4 uint32

%% 1-14 浮点型参与的运算
clear all;
a = uint16(256);
b = single(32.548);
z = 120.19;
% A = a * b % 错误使用 * 整数只能与同类的整数或双精度标量值组合使用。
% single类型的变量不可以和整型变量相乘,但是double类型的变量可以。
B = a * z % 整型变量可以和double类型变量相乘,结果为原本的那个整型变量
C = b * z % single类型的变量可以和double类型变量相乘,结果为single类型变量
str1 = 'MATLAB~~'; % 字符串的每个字符都可以转换成一个数字,是原本的阿斯克码
STR1 = str1 - 32 % 强制类型转换为阿斯克码所对应的值
whos
%% 实验结果
B =
uint16
30769
C =
single
3.9119e+03
STR1 =
45 33 52 44 33 34 94 94
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
B 1x1 2 uint16
C 1x1 4 single
STR1 1x8 64 double
a 1x1 2 uint16
b 1x1 4 single
str1 1x8 16 char
z 1x1 8 double

%% 1-15 创建复数
a = pi + 5i % 虚部可以直接用i或j,可以不用写乘号
b = pi + 5*j % 用i和j的效果完全一样,j也会被自动转换成i
a == b % 比较a,b是否相同,返回1则表示相同,0则表示不同(输出为1,说明a和b是相同的)
%% 实验结果
% ex1_15
% a =
% 3.1416 + 5.0000i
% b =
% 3.1416 + 5.0000i
% ans =
% logical
% 1

%% 1-16 复数的操作函数
x = rand(3) % 产生一个3阶矩阵,矩阵中的各个值都为满足N(0,1)的数的结果
y = rand(3) % 产生一个3阶矩阵,矩阵中的各个值都为满足N(0,1)的数的结果(因为是随机数,所以每次都不一样)
z = complex(x,y) % 输入实部和虚部,以x为实部,y为虚部的创建复数z
zr = real(z) % 提取复数矩阵z的实部
zi = imag(z) % 提取复数矩的z的虚部
za = abs(z) % 求复数矩阵z的模长
zan = angle(z) % 求复数矩阵z的幅角
%% 实验结果
% ex1_16
% x =
% 0.8003 0.9157 0.6557
% 0.1419 0.7922 0.0357
% 0.4218 0.9595 0.8491
% y =
% 0.9340 0.7431 0.1712
% 0.6787 0.3922 0.7060
% 0.7577 0.6555 0.0318
% z =
% 0.8003 + 0.9340i 0.9157 + 0.7431i 0.6557 + 0.1712i
% 0.1419 + 0.6787i 0.7922 + 0.3922i 0.0357 + 0.7060i
% 0.4218 + 0.7577i 0.9595 + 0.6555i 0.8491 + 0.0318i
% zr =
% 0.8003 0.9157 0.6557
% 0.1419 0.7922 0.0357
% 0.4218 0.9595 0.8491
% zi =
% 0.9340 0.7431 0.1712
% 0.6787 0.3922 0.7060
% 0.7577 0.6555 0.0318
% za =
% 1.2300 1.1793 0.6777
% 0.6934 0.8840 0.7069
% 0.8672 1.1620 0.8497
% zan =
% 0.8623 0.6817 0.2554
% 1.3647 0.4597 1.5203
% 1.0629 0.5993 0.0375

%% 1-17 无穷量Inf与非数值量NaN
x = 1/0 % 任何大于0的数除以0都是一个正无穷大,任何小于0的数除以0都是一个负无穷大
y = exp(1000) % e的1000次方实在是太大了,数组装不下,直接被当成无穷大处理
z = log(0) % log(0+)的值会无限接近负无穷大,那么log(0)会被视为负无穷大
v = inf % 构造一个无穷大的数
a = 0/0 % 0除以0是一个非数值量
b = NaN % 构造一个非数值量
c = NaN('single') % 创建单精度浮点类型的非数值量
m = 3i/0 % 虚部除以0,那就可以得到虚部的无穷大,实部为0
a == b % 非数值量与非数值量之间不能认为是相等的
%% 实验结果
% ex1_17
% x =
% Inf
% y =
% Inf
% z =
% -Inf
% v =
% Inf
% a =
% NaN
% b =
% NaN
% c =
% single
% NaN
% m =
% 0.0000 + Infi
% ans =
% logical
% 0

%% 1-18 创建逻辑类型
clear all;
a = [true true false false true] % 一个逻辑类型的数组,逻辑类型为true和false
x = randn(4) > 0.9 % randn表示一个满足N(0,1)正态分布的随机数,是否大于0.9,如果是,输出1;如果不是,输出0
whos % 它的类型是logical
x = [1 4.7 pi nan inf 10]
y = isinf(x) % x里面的每一个值是否为无穷大?
%% 实验结果
% ex1_18
% a =
% 1×5 logical 数组
% 1 1 0 0 1
% x =
% 4×4 logical 数组
% 1 0 0 0
% 1 0 0 0
% 0 0 0 0
% 0 1 1 1
% Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
%
% a 1x5 5 logical
% x 4x4 16 logical
%
% x =
% 1.0000 4.7000 3.1416 NaN Inf 10.0000
% y =
% 1×6 logical 数组
% 0 0 0 0 1 0

%% 1-19 将短字符串合并成长字符串
% 在'abc'和'abcd'的末尾分别补2个和1个空格
A = ['abc '; 'abcd '; 'abcde']
% 不在字符串字符补空格,直接合并不同长度的字符串,系统报错,提示用户没行列数不等
% B = ['abc'; 'abcd'; 'abcde'] % 要串联的数组的维度不一致。
% 利用char创建字符数组,可按照最长字符串的长度,自动把长度不够的字符末尾补空格,使所有的字符串相同。
C = char('talent', ' + ', 'hard-working')
% 与函数char相反,如果用户希望从一个字符数组中抽取某一字符串,可以调用deblank函数
D = deblank(C(3,:))
%% deblank的含义
% deblank - 删除字符串末尾的尾随空白
% 此 MATLAB 函数 将从 str 中删除尾随空白和空字符,并以 newStr 形式返回结果。但
% 是,deblank 不会删除实义空白字符。例如,deblank 将删除尾随空格和制表符,但不
% 会删除不间断空白字符 char(160)。
%
% newStr = deblank(str)
%% 实验结果
% ex1_19
% A =
% 3×5 char 数组
% 'abc '
% 'abcd '
% 'abcde'
% C =
% 3×12 char 数组
% 'talent '
% ' + '
% 'hard-working'
% D =
% 'hard-working'

%% 判断两个字符数组中的每个元素是否相同
str1 = 'Matlab'
str2 = 'MATLAB'
str1 == str2 % 每个字符都会比较,区分大小写
%% 实验结果
% ex1_20
% str1 =
% 'Matlab'
% str2 =
% 'MATLAB'
% ans =
% 1×6 logical 数组
% 1 0 0 0 0 0

%% 1-21 使用函数比较字符数组
strcmp('human','HUMAN') % strcmp:比较两个字符串是否相等(区分大小写)
strcmpi('human','HUMAN') % strcmpi:比较两个字符串是否相等(不区分大小写)
A = {'Handle Graphics', 'Statistics'; ...
' Toolboxs', 'MathWorks'};
B = {'Handle Graphics', 'Signal Processing'; ...
'Toolboxs', 'MATHWORKS'};
match1 = strcmp(A,B)
match2 = strncmp(A,B,2) % strncmp:比较两个字符串前n个字符是否相等(区分大小写)
match3 = strncmpi(A,B,2) % strncmpi:比较两个字符串前n个字符是否相等(不区分大小写)
%% 实验结果
% ex1_21
% ans =
% logical
% 0
% ans =
% logical
% 1
% match1 =
% 2×2 logical 数组
% 1 0
% 0 0
% match2 =
% 2×2 logical 数组
% 1 0
% 0 0
% match3 =
% 2×2 logical 数组
% 1 0
% 0 1

%% 1-22 字符串查找与替换演示
s = 'Find the starting indices of the shorter string.';
findstr(s, 'the') % 在字串s中查找'the'
findstr('the', s) % 查找s中的字符串'the'
strfind(s, 's') % 查找s中字符s
strrep(s, 'Find', 'FIND') % 将字符串中的Find换成FIND
x = strmatch('max', char('max', 'minimax', 'maximum')) % 查找匹配指定字符串
%% 实验结果
% ex1_22
% ans =
% 6 30
% ans =
% 6 30
% ans =
% 10 25 34 42
% ans =
% 'FIND the starting indices of the shorter string.'
% x =
% 1
% 3

%% 1-23 将数值类型换成为字符串类型演示例子
int2str(eye(3)) % eye指的是单位矩阵,int2str指将正整数数值转换为等值字符
num2str(randn(2,2),3) % 把数值类型数据转换成指定精度和形式的字符类型
x = [3.85 2.91; 7.74 8.99]
A = mat2str(x) % 把数值类型的数据转换成指定精度和形式的字符类型,并返回MATLAB可以识别的格式
dec2hex(1023) % 十进制转十六进制
dec2bin(23) % 十进制转二进制
%% 实验结果
% ex1_23
% ans =
% 3×7 char 数组
% '1 0 0'
% '0 1 0'
% '0 0 1'
% ans =
% 2×15 char 数组
% ' 1.42 0.198'
% '0.292 1.59'
% x =
% 3.8500 2.9100
% 7.7400 8.9900
% A =
% '[3.85 2.91;7.74 8.99]'
% ans =
% '3FF'
% ans =
% '10111'

%% 1-24 字符串转换为数值类型实例演示
str2num('2 4 6 8') % 把字符串转换成数值数组
str2num('[2 4 6 8]') % 把字符串转换成数值数组,忽略掉中括号
str2double('123.45e7') % 把字符串转换成double型
str2double({'2.71', '3.1415'}) % 将字符串数组转换成double型数组
hex2num('400921fb54442d18') % 把字符类型数据转换成指定精度和形式的数值类型
hex2dec('3ff') % 将十六进制的字符类型转换成正整数
%% 实验结果
% ex1_24
% ans =
% 2 4 6 8
% ans =
% 2 4 6 8
% ans =
% 1.2345e+09
% ans =
% 2.7100 3.1415
% ans =
% 3.1416
% ans =
% 1023
% ex1_24
% ans =
% 2 4 6 8
% ans =
% 2 4 6 8
% ans =
% 1.2345e+09
% ans =
% 2.7100 3.1415
% ans =
% 3.1416
% ans =
% 1023

%% 1-25 求曲线长度,曲线是一个参数方程
% x(t) = \sin(2t)
% y(t) = \cos(t)
% z(t) = t
% t ∈[0, 3\pi]
% 根据高等数学中曲线长度的求法,可列出求该曲线长度的表达式为:
% f(t) = \int^{3\pi}_{0}{4\cos^2(2t)+\sin^2(t)+1}dt
clear all;
t = 0:0.05:3*pi; % 变量取值,步长为0.05
plot3(sin(2*t), cos(t), t); % 用plot3函数绘制曲线图形,效果如图所示
%% 需要编写一个函数文件才能让它求曲线长度
% 1-25附属函数(是另一个文件):
% function f = ex1_25_func(t)
% f = 4*cos(2*t).^2 + sin(t).^2 + 1;
% end
% 利用积分函数quad求出曲线长度
len = quad('ex1_25_func',0,3*pi)
%% 实验结果
% ex1_25
% len =
% 32.9867
1-25的内联函数
%% 1-25附属函数:
function f = ex1_25_func(t)
f = 4*cos(2*t).^2 + sin(t).^2 + 1;
end